Belfast and the Exhibition of its Most Famous Legacy
/Titanic Belfast - the world's largest attraction dedicated to the ill-fated ocean liner. Image Credit: William Murphy via Flickr CC
If London was the first UK city I had known about, then Belfast was the second one thanks to its notoriety as the birthplace of the RMS Titanic, which has been a long-time interest of mine and remains a significant part of Belfast’s story.
That story has been a long and complex one which begins with the settlement of the area in the northeast corner of Ireland during the Bronze and Iron ages, out of which still remain a 5,000 year old henge (older than the more notable Stonehenge in Wiltshire) known as Giant’s Ring and a couple of fort hills. Belfast became substantially established in the 17th Century during the migration of English and Scottish settlers, and the city was granted borough status by James VI & I in 1613. Through the 18th and 19th centuries, Belfast grew rapidly and went through a series of expansions to straddle between County Down and County Antrim as it became a thriving industrialized and commercial city with wealth generated through linen, rope-making, tobacco, heavy engineering, and shipbuilding – most significantly Harland and Wolff’s, which was one of the largest shipyards in the world.
Belfast gained city status under Queen Victoria in 1888 and continued to prosper, but became politically divided over the issue of Irish Home Rule and eventually became the capital of Northern Ireland when Ireland was partitioned and the six counties of Northern Ireland elected to remain part of the United Kingdom. Within the city, there has been sectarian tension between its unionist/loyalist (usually Protestant) and nationalist/republican (usually Catholic) communities. This grew into a civil conflict known as “the Troubles” from 1969 to 1998 and resulted in the violent deaths of over 1,600 people, which combined with the decline of industry following World War II, saw the city suffer economically.
The Good Friday Agreement of 1998 provided the political basis for ending the vast majority of the violence and since then, Belfast has largely moved forward in peace. As well as being the capital and largest city of Northern Ireland, Belfast is the second-largest city on the island of Ireland and the 10th-12th largest city in the United Kingdom. It is a center for higher education, business, industry, arts, and tourism, and its central area has undergone expansion and regeneration, so that it has achieved growth and is the economic engine of Northern Ireland.
Part of that regeneration has come in the form of Titanic Quarter, an area of land located just to the east of the city center on Queen’s Island which once belonged to Harland & Wolff and home to the facilities which produced the Titanic and other vessels of the White Star Line. All but derelict by the end of the 20th Century, it has been transformed over the last decade into a mixed-use development at the center of which is Titanic Belfast. Opened in 2012 and visited by Her Majesty the Queen for the Titanic centennial (and her Diamond Jubilee), it not only stands as the largest Titanic-themed attraction in the world, but also as a monument to Belfast’s maritime heritage. The exterior takes on the appearance of the angled prows of ships in a nod to the great liners built there and is mostly clad in aluminum shards, so that it looks – interestingly enough – like an iceberg.
The expansive Main Atrium of Titanic Belfast. Image Credit: Titanic Belfast via Flickr CC
Stepping into the main atrium of the structure (which is home to Ireland’s longest freespan escalator at over 80 feet long), this heritage is commemorated with a compass on the floor around which are lines from Thomas Garnduff’s 1924 poem, Songs from the Shipyard. Indeed, it feels as like stepping into another world – when shipbuilding and heavy industry was king, this is also visibly seen with a 60 foot wall of rusted steel plates like the ones used for Titanic, as well as the names of all the vessels built by Harland and Wolff across from it. There's also a platform overlooking the atrium which mimics the Titanic's prow and may therefore provide for a Jack and Rose moment.
From here, one can start a journey through the main exhibition, which is the Titanic Belfast Experience and features nine interpretive and interactive galleries telling the story of the Titanic, her sister’s Olympic and Britannic (collectively called the Olympic-class ships), and the city and shipyard which built them.
Harland & Wolff gates and White Star Line posters greet visitors as they begin the Titanic Experience with Boomtown Belfast. Image Credit: Titanic Belfast via Flickr CC
The first gallery is Boomtown Belfast, which gives visitors the atmosphere of Belfast at the turn of the 20th Century as a city of industrial prosperity and political tension. Through an original set of Harland & Wolff gates are interactive maps and scale models of the Titanic, as well as a game to see how many rivets can be “fit” in 30 seconds. This leads to gallery two in the form of The Shipyard, where one is immersed into the sights, sounds, and even smells of the construction of Olympic and Titanic.
Scale replica sections of Titanic's bow and rudder, as well as the Arrol Gantry as part of The Shipyard gallery. Image Credit: All Titanic Belfast (Left, Top Right, and Lower Right) via Flickr CC; Collage by Wesley Hutchins via Photo Collada
An elevator (or lift, as they were called at the time) carries visitors to the top of a 66-foot scaffold alluding to the Arrol Gantry which aided in the construction of the sister ships, and from here, they are transported via a cart on a ride through other recreated elements of the shipyard, scale replica sections of Titanic’s rudder and bow, as well as photos and motion picture footage depicting what it took to build the biggest ships in the world. Gallery three – The Launch marks the completion of Titanic’s hull and her launching into the River Lagan with a large window showing the finished hull on the slipway before clearing away to show the area as it appears to today.
With the empty hull in the water, visitors move on to the fourth gallery, called The Fit-Out, which features the great vessel going through her final stages of construction as she is fitted out to become a luxury liner. There are examples of cabins from each class, a scale model of the ship, information panels and large pictures of the interiors, and most impressively, a 360-degree CGI tour of the ship – going through seven levels from the engine room to the navigation bridge (seen in the above video). This leads to experiencing life aboard the ship itself in the fifth gallery – The Maiden Voyage. Here, visitors can walk on the deck, have a seat on a bench, and take in the views of Belfast Harbour while also viewing the famous photos taken by Father Francis Browne aboard the ship during his overnight passage on the first leg of the voyage from Southampton to Queenstown (now Cobh) via Cherbourg, France.
Gallery featuring Father Browne's collection of photos and deck benches with views of the harbor and atrium, as if on Titanic herself. Image Credit: Titanic Belfast (Top Left and Bottom Right) via Flickr CC
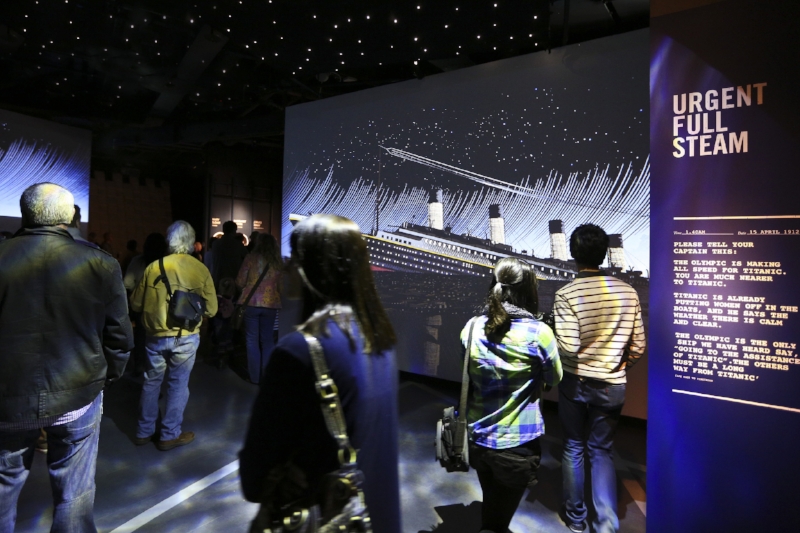
Of course, the happiness and good feeling doesn’t last as Titanic hits an iceberg and sinks to the bottom of the Atlantic with a great loss of life. For this, galley six – The Sinking features a cold room and simulated water to immerse the visitor into the conditions experienced by the Titanic and the souls aboard her that night in 1912. The beeping Morse Code signals carrying Titanic’s distress call in form of CQD and SOS are heard, as well as audio from survivors giving their gripping accounts of the unfolding disaster, accompanied by the images of the great liner foundering.
Graphic novel-like depiction of the sinking Titanic. Image Credit: Titanic Belfast via Flickr CC
Also depicted is the confusion and contradictory reporting reports in the media during the early hours following the sinking. This leads into the seventh gallery of The Aftermath, where there is a full-sized replica lifeboat on which a large double-sided television screen displays the portrayals of the American and British inquiries into the disaster. There are also interactive tablets allowing people to search a database and see if they had a relative on board, as well as information on Harland and Wolff to the present day and careers of Titanic’s sister ships.
The Aftermath Gallery featuring a replica lifeboat and representation of the present-day Harland and Wolff gantry cranes. Image Credit: Titanic Belfast via Flickr CC
Following this, the Myths and Legends section in gallery eight deals with Titanic in popular culture, including books, plays, poems, films, songs, and other media that have been inspired by the ship for over a century. Clips and excerpts from these are featured, along with various Titanic memorabilia as Celine Dion’s My Heart Will Go On plays in the background. There are also more interactive tablets, this time providing answers to long-standing myths surrounding the Titanic.
Myths and Legends meet reality as Titanic appears on various Media. Image Credit: Titanic Belfast via Flickr CC
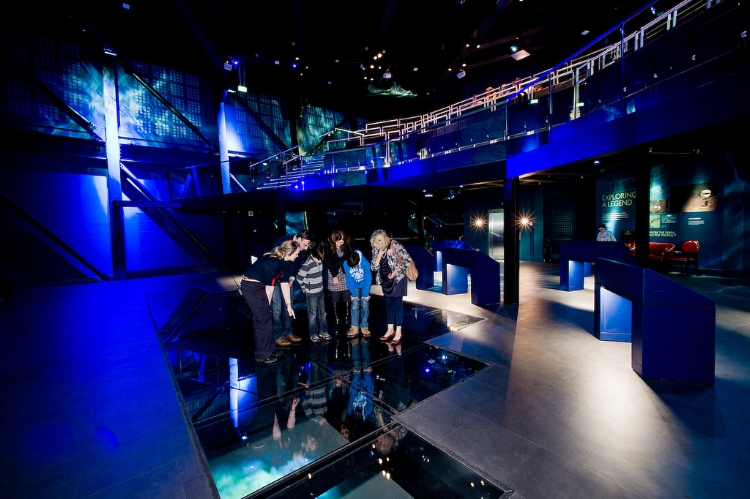
The ninth and final gallery is Titanic Beneath, which brings Titanic’s story up to the present with the discovery of her wreck by Dr. Robert Ballard, and a video about the discovery and exploration of the wreck is available for viewing in an experience made to feeling as though the visitor is underwater. Further on is a glass floor revealing a mosaic of the Titanic floating underneath as she appears today on the ocean floor, as well as more information of the wreck and the debris around it.
Looking two-and-a-half miles "down" to the Titanic's final resting place in the ninth gallery of the Titanic Belfast Experience. Image Credit: Titanic Belfast via Flickr CC
Under this is the Ocean Exploration Centre, which features additional experiences with regard to Titanic as well as an educational facility drawing on expertise and resources from local universities, with a marine biologist on hand and a focus on the waters of Northern Ireland and images from Dr. Ballard’s expeditions throughout the world in the hope that Titanic may spawn interest in this area of study for future generations.
The Ocean Exploration Centre. Image Credit: all Titanic Belfast ( Top Left, Top Middle, Top Right, Bottom Left, and Bottom Right) Via Flickr CC; Collage by Wesley Hutchins via Photo Collada
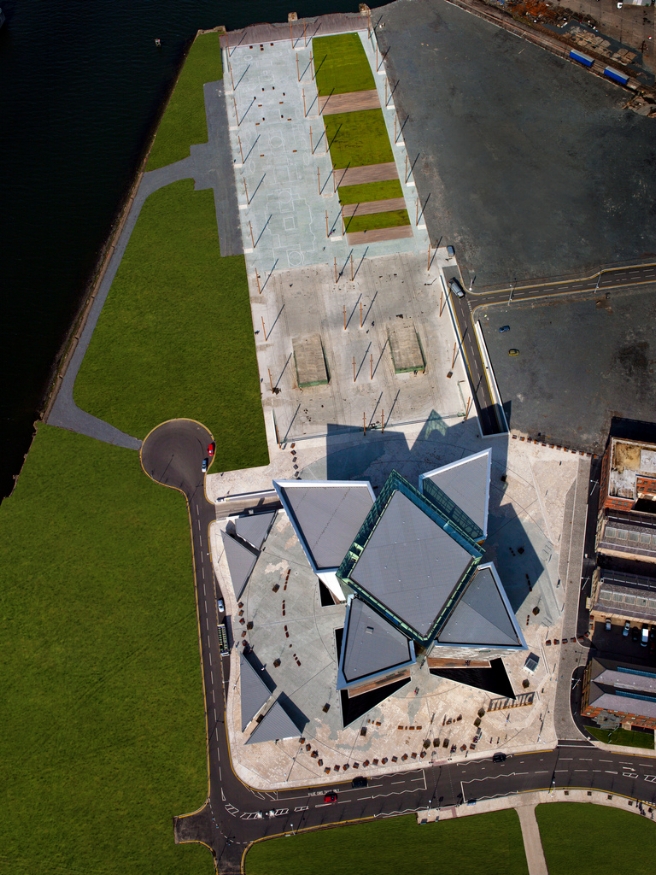
This whole experience can be done in 2-3 hours, though Titanic aficionados may naturally spend more time. In addition to the main exhibition, the building also features gift shops with Titanic memorabilia (including plates with the White Star Line logo), places to eat, and areas for booking events such as conferences and receptions – including a room featuring a stylized replica of the Grand Staircase. In the greater expanse of Titanic Quarter, there are the slipways on which Titanic and her sister’s were built – which have been turned into a nice walking plaza, the SS Nomadic – the last White Star liner and one of the tenders which serviced Titanic at Cherbourg, the Drawing Offices where the vessels were designed, Titanic Studios (where Game of Thrones is filmed), the Thompson Graving Dock, which was built to accommodate Titanic for dry-docking purposes, and nearby are the modern-day facilities of Harland and Wolff – dominated by the yellow gantry cranes, Samson and Goliath. Furthermore, within the the plaza which surrounds the Titanic Belfast building, there is a large map of the Northern Hemisphere which shows Titanic's maiden voyage track and features benches which form a Morse Code sequence which reads: “DE (this is) MGY MGY MGY (Titanic’s call sign) CQD CQD SOS SOS CQD (the distress calls radioed from the ship)”.
Aerial view of Titanic Belfast, with the slipways (Olympic's on the right and Titanic's on the left) above it and the Drawing Offices to the Right. Image Credit: Titanic Belfast via Flickr CC
Titanic Belfast is open year-around save for Christmas Eve, Christmas Day, and Boxing Day (December 24-26) and times vary depending on the season. Tickets can be purchased for the main exhibition experience alone or for the Titanic Discovery Tour, a walking tour of the slipways, Drawing Offices, and other features in the immediate area of Titanic Belfast. Visitors can also join in special events for afternoon tea and Christmas. There's also the White Star Premium Pass to access the main experience, the Discovery Tour, and the Nomadic, which ought to make make for an exciting, educational, and memorable experience.
For Belfast and its citizens, a memorable experience is exactly what they want visitors to have as the city strives to march forward confidently into the future. What’s remarkable is that until fairly recently, Titanic was not embraced so much by the city, for it was considered a mark of shame to have built a vessel that sank on its only voyage less than a fortnight after leaving her birthplace. With the discovery of the wreck and further confirmation that Titanic was a liner of sound workmanship, the city has done more to promote its connection to her, which has led to a cheeky saying that “she was fine when she left.” The popularity of James Cameron’s 1997 film helped bring Titanic to a new generation, as well as increased interest in Belfast, so that Titanic Belfast is in many ways, the culmination of the city’s reconnection with and pride in its most famous product, as well as sign of its renewal and regeneration. This reached new levels of success this year with the attraction welcoming its three millionth visitors and being named the Leading Visitor Attraction in Europe by the prestigious World Travel Awards – the “Tourism Oscars” – and seeing off competition such as the Eiffel Tower. Through Titanic, Belfast is indeed continuing to build for itself a positive reputation and showing that it is turning a corner in its long and layered history.
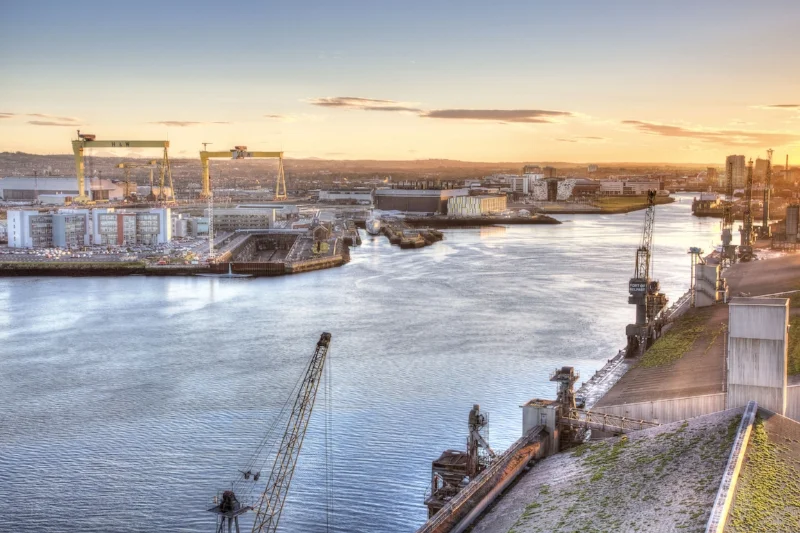
Grand View of the River Lagan, Belfast Harbour, the city itself and beyond. At Left are the gantry cranes of Harland & Wolff, Samson and Goliath; below them is the Thompson Graving Dock, were Titanic was partly fitted out; to the right is Titanic Studios in the large brown building, and further over is Titanic Belfast and the slipways. Image Credit: Titanic Belfast via Flickr cc